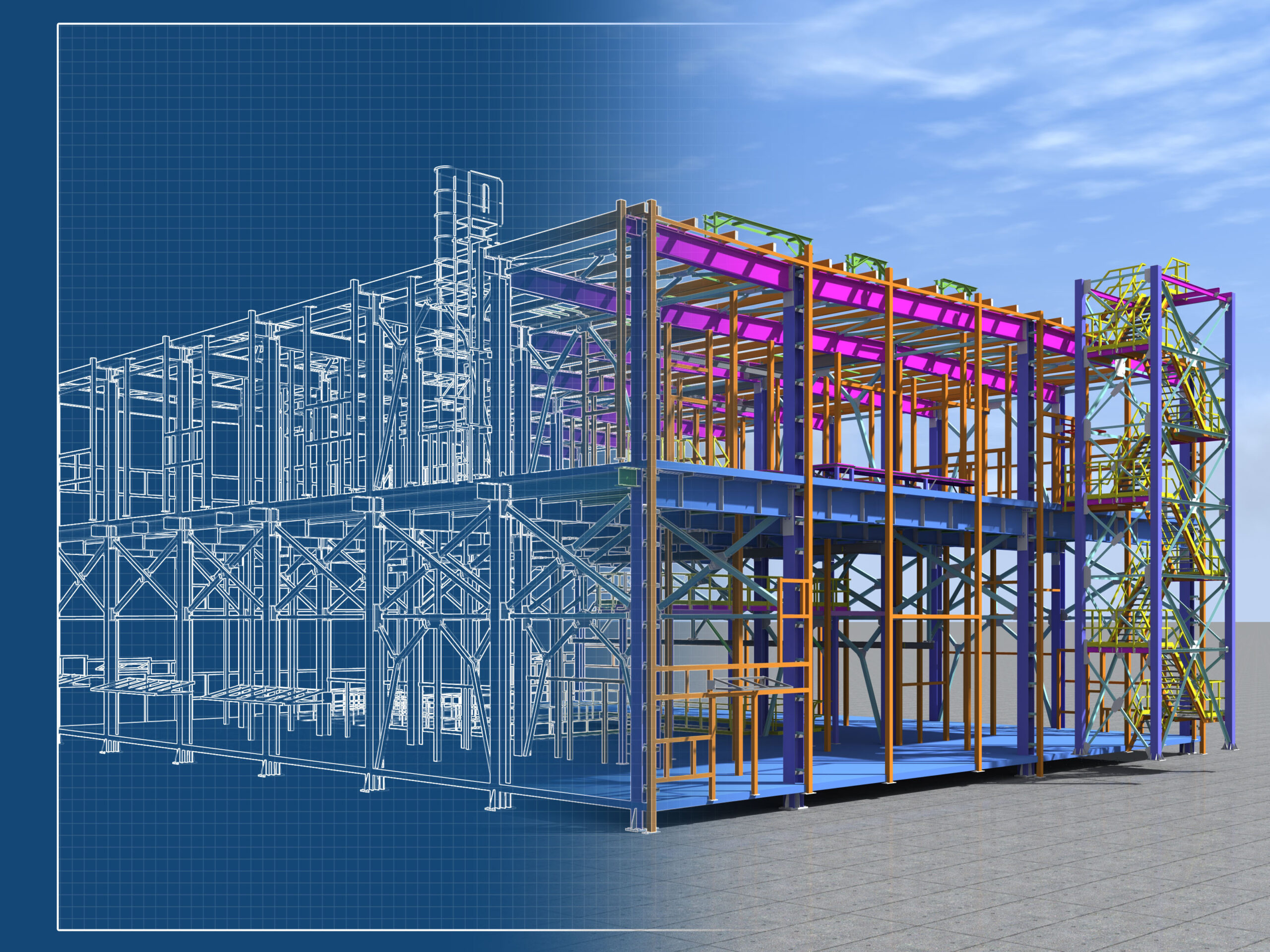
Numerous digital engineering applications that shape the future of as-built documentation, product development, manufacturing, quality assurance, and production begin with 3D laser scanning. 3D scanners combine sophisticated hardware with specialized software to create highly detailed and accurate three-dimensional representations of objects, environments, or landscapes.
For those still relying on mechanical tools and conventional coordinate measuring machine (CMM) technology, 3D laser scanning technology is an accessible entry point into advanced manufacturing and engineering methodologies.
What Is 3D Scanning Technology?
3D laser scanning technology is a non-contact, high-precision technology that uses LiDAR (light detection and ranging) to measure and record distances to surfaces. The result is a comprehensive digital model known as a point cloud, which represents the scanned object’s surface geometry with millimeter-level accuracy.
Image Source: ATT Metrology Solutions
Data collected by 3D laser scanners is invaluable in design, asset management, prefabrication, and facility modifications. Precision as-built laser scans, for instance, have huge benefits for construction companies that rely on accurate depictions of current site conditions.
What Is the Difference Between 3D Laser Scanning and Other Scanning Technologies?
While 3D laser scanning shares similarities with traditional imaging techniques, such as photogrammetry and structured light scanning, its ability to capture highly accurate, dense data points using laser beams makes it stand out.
- Laser Scanning vs. Photogrammetry: What is 3D scanning technology vs. photogrammetry? Photogrammetry pieces together photographs of as-built conditions and weaves in GPS coordinates to create a 3D model. 3D laser scanning, on the other hand, uses laser beams to directly capture data points, offering more precise measurements, especially for complex surfaces.
- Laser Scanning vs. Structured Light Scanning: Structured light scanning uses projected light patterns to capture thousands of points simultaneously, making it ideal for complex organic shapes such as automotive body panels. Meanwhile, 3D laser scanning relies on laser beams that are emitted and reflected to collect spatial data. The technology’s ability to scan extensive areas and large objects from a distance makes it indispensable in construction and large-scale industrial applications.
How Does 3D Laser Scanning Work?
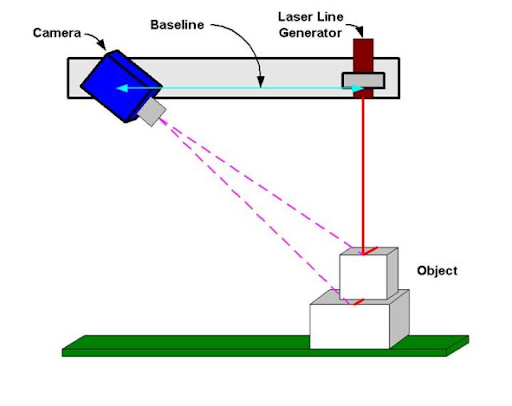
3D laser scanning works much like bat echolocation. It emits laser pulses or beams and measures the time it takes for the light to bounce back from surfaces in the scanned environment.
Image Source: engineering.com
Here’s how does 3D laser scanning work in detail:
- Emitting Laser Beams – The 3D laser scanning technology emits laser beams and sweeps over the structure or object. These beams bounce back to the scanner after hitting the surface, and the scanner measures the time it takes for the light to return, calculating the distance traveled.
- Capturing Data Points – The scan produces innumerable coordinates, each containing an X, Y, and Z value associated with its distance and position in space.
- Creating a Digital 3D Model – These data points are then used to generate a 3D digital model called a “point cloud.” The point cloud is a collection of all the data points captured during the scanning process, and it serves as the basis for creating a highly detailed 3D representation of the object or environment. The denser the point cloud, the more accurate and detailed the final 3D model.
Applications of 3D Laser Scanning
The accuracy of 3D laser scanning technology is measured in millimeters, which makes it incredibly useful for industries that require high precision, such as aerospace and engineering.
By employing this technology at the onset of a project, AEC (architects, engineering, and construction) professionals can capture and access precise data, drawings, and models to expedite design planning, asset management, prefabrication, and facility modifications.
Below are some useful applications for 3D laser scanning:
-
Manufacturing and Prototyping
3D laser scanning is used to capture the exact dimensions of prototypes or parts for reverse engineering and quality control. It helps manufacturers create precise digital models, ensuring the final product meets design specifications. By quickly scanning physical objects, manufacturers can detect design flaws early in the process, saving time and reducing costs.
-
Construction and Architecture
3D laser scanning can precisely capture as-built data of existing structures, piping, equipment, or manufacturing processes for new designs, retrofitting, or maintenance. This enables accurate site analysis, which allows construction companies to create detailed digital models of existing structures or sites.
-
Healthcare (e.g., Prosthetics Design)
In healthcare, particularly in prosthetics design, 3D laser scanning helps create custom prosthetic limbs that perfectly match the patient’s body. By scanning a patient’s residual limb, a 3D model is created, which can then be used to design a personalized prosthetic that fits comfortably and functions optimally.
-
Forensics and Archaeology
3D laser scanning is also used in forensics and archaeology to capture crime scenes or ancient artifacts. Forensic teams can create digital models of crime scenes for further analysis, while archaeologists use scanning to preserve delicate artifacts and historical sites, ensuring they are documented in 3D for future study.
Benefits of Using 3D Laser Scanning Technology
The adoption of 3D laser scanning technology brings numerous advantages to industries looking for precision and efficiency. Here are some key benefits:
- Speed and Efficiency: Traditional measurement methods can be slow and prone to errors. 3D laser scanning allows for rapid data capture, significantly speeding up processes like surveying or quality control.
- Enhanced Accuracy and Detail: By capturing millions of data points, 3D laser scanning ensures even the most complex geometries are measured with incredible accuracy.
- Cost-Effectiveness: 3D laser scanning reduces the need for physical prototypes and manual measurements, helping businesses save on time, labor costs, and materials.
- Environmental Sustainability: 3D laser scanning minimizes the need for rework and waste, contributing to more sustainable practices in industries like construction and manufacturing.
Challenges and Limitations
While 3D laser scanning technology provides groundbreaking precision and efficiency across industries, it does come with a few challenges.
- High Initial Investment Costs
One of the primary hurdles is the initial cost of setting up these systems. High-precision 3D laser scanners, essential for achieving detailed and accurate results, can be expensive. This upfront investment may pose a barrier for small businesses or organizations with limited budgets. However, the investment often proves worthwhile when considering the long-term benefits, such as enhanced efficiency, reduced project timelines, and minimized errors. - Limitations in Outdoor Environments
Another significant limitation lies in environmental factors. For example, weather conditions such as rain, fog, or extreme temperatures can interfere with the performance and accuracy of 3D laser scanning equipment. Reflective or transparent surfaces, such as glass or water, can also distort scan results, making achieving reliable data in certain settings challenging. These issues can be particularly problematic for outdoor projects or when scanning environments with complex surface materials.
Fortunately, ongoing advancements in 3D scanner technology are helping to address these challenges. Modern systems are increasingly being designed to perform reliably under diverse environmental conditions and to mitigate the effects of reflective surfaces. These innovations continue to expand the usability and effectiveness of 3D laser scanning across a wide range of industries and applications.
Embrace a New Era of Efficiency With 3D Laser Scanning
ATT Metrology’s 3D laser scanning services deliver an impressive 2-4mm precision across applications. Whether you’re designing prototypes, performing quality control, or conducting complex inspections, we have the tools and expertise to support your project.
Capture intricate architectural details and map vast landscapes with greater accuracy. Contact us today for more information on our 3D laser scanning services.